where \(x\in \mathbb{R}\) in each case.
- Find the solution set, \(S\), of the inequality \(f(x)\ge g(x).\)
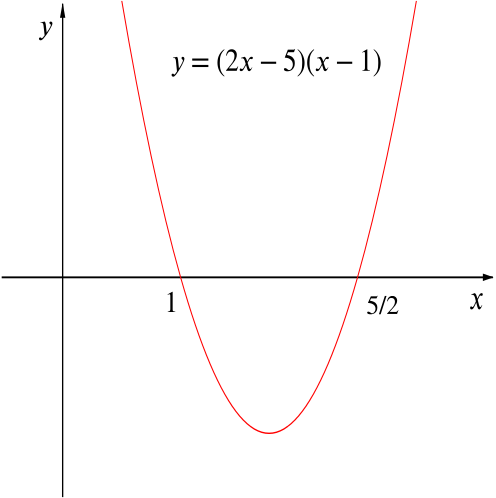
By considering the graph of \(y=(2x-5)(x-1)\), we see that the solution is \(1\le x\le \tfrac{5}{2}.\)
- Sketch the graph of \(y=f(x)-g(x)\) for \(x\in S\), and state the greatest and least values of \(f(x)-g(x)\) for \(x\in S\).
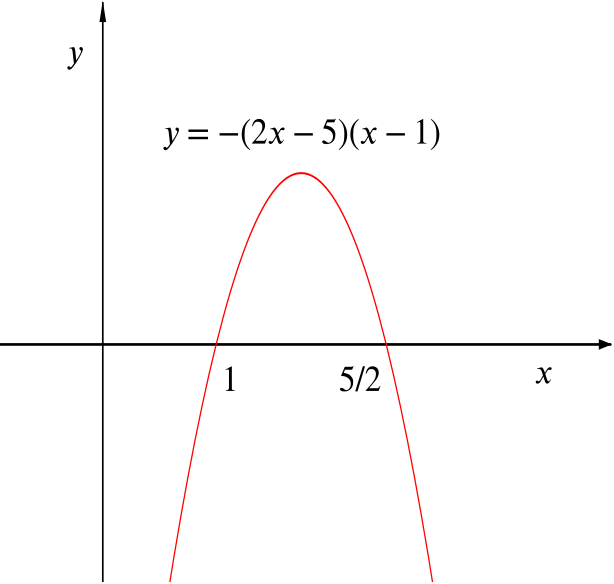
Using our working from above, \(f(x)-g(x)=-(2x-5)(x-1)\), so the graph of \(y = f(x) - g(x)\) looks like this:
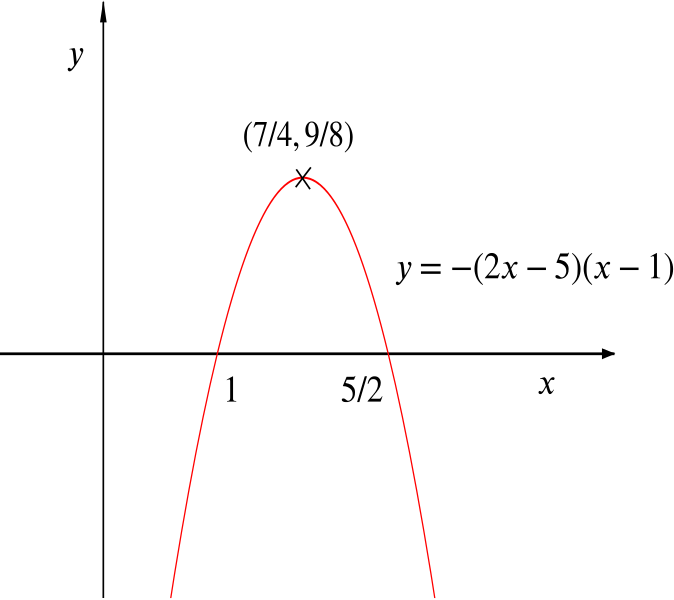
Since \(S\) is the set of \(x\) such that \(f(x)-g(x)\ge 0\), the minimum value of \(f(x)-g(x)\) on \(S\) must be zero, when \(x = 1\) or \(\dfrac{5}{2}\).
To find the maximum, we can complete the square: \[\begin {align*} -2x^2+7x-5 &= -2\left(x-\frac{7}{4}\right)^2+\frac{49}{8}-5\\ &=-2\left(x-\frac{7}{4}\right)^2+\frac{9}{8}. \end {align*}\]Since \(2\left(x-\frac{7}{4}\right)^2 \ge 0\), we have \(-2x^2+7x-5\le \tfrac{9}{8}\), so the maximum value of \(f(x)-g(x)\) on \(S\) is \(\tfrac{9}{8}\), and this is attained at \(x=\frac{7}{4}\). So we can sketch \(f(x)-g(x)\) on \(S\).
Alternatively we can say that \(y = f(x) - g(x)\) has its maximum when \(x = \dfrac{1 + \dfrac{5}{2}}{2}\), or \(\dfrac{7}{4}\).
Now \(y = \dfrac{9}{8}\) when \(x=\dfrac{7}{4}.\)